5 tips to improve accuracy in drone mapping projects
One of the biggest frustrations you can face in a drone mapping project is the realization that the data you’ve captured isn’t fit for purpose.
No one wants to spend valuable time and resources collecting images which don’t give you the answers you’re looking for. While you can't guard against every possible issue, a little planning can go a long way towards improving results.
We’ve rounded up five tips to improve the accuracy of your drone mapping projects.
1. Know the distance
Before you capture any images, you need to know the level of detail required for your project. Calculate the ground sampling distance (GSD) you want to capture and plan your flights accordingly.
This step is vital because the accuracy of a measurement is directly related to the ground sampling distance of the original images – so take the time to double-check it’s right.
If you’re not sure what your ground sampling distance will be with your camera, we have an article which will get you started. You can find all of the basic camera model parameters you need in the Internal Camera Model Parameters section of one of your latest Quality Reports. If you’re using Pix4Dcapture, this will be calculated automatically.
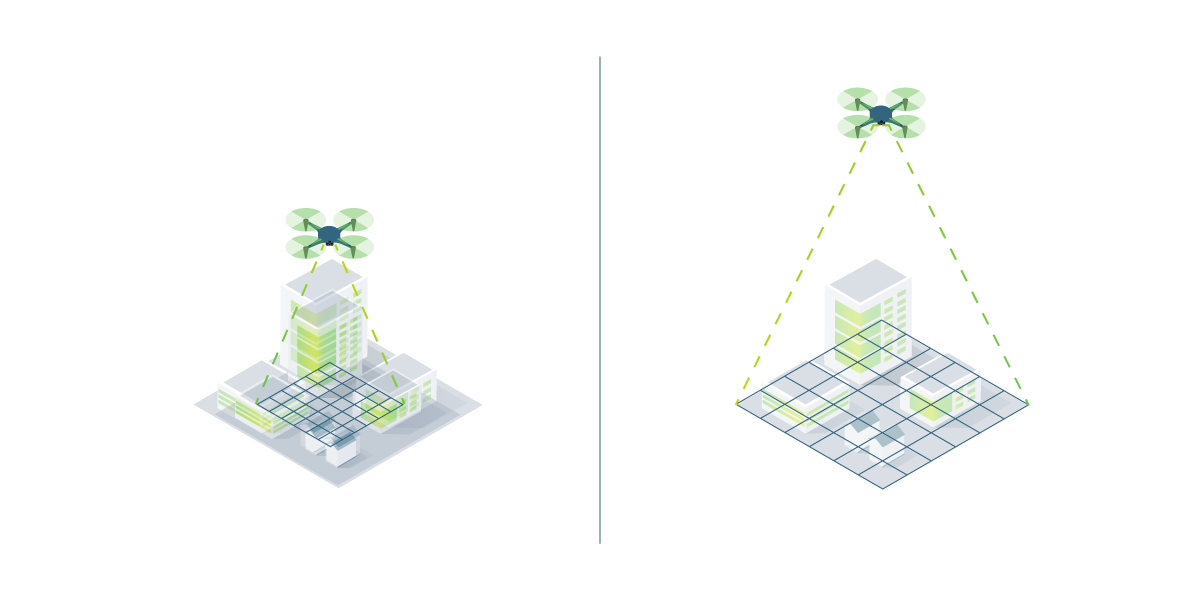
2. Capture enough overlap
Plenty of image overlap between images will give better results. We recommend that images overlap with each other by at least 75% in the front and 60% on each side.
If you are not confident that you have sufficient image overlap, consider capturing more. Remember, you can remove extra information but cannot create something from nothing.
For more details, check out this article on choosing the appropriate amount of overlap.

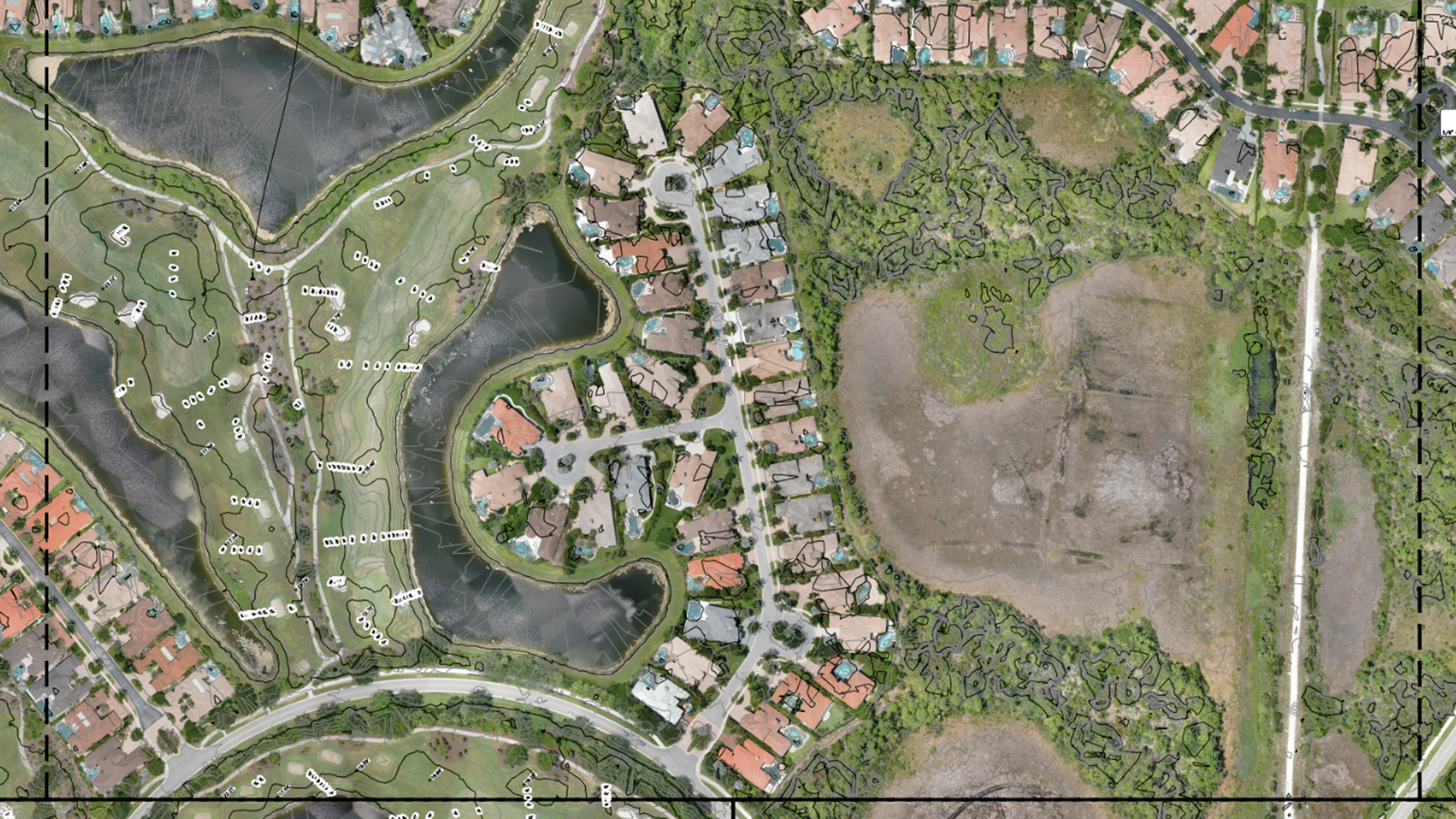
3. Expand the area captured
Ensure you capture images slightly beyond the extent of the area of interest.
The reconstruction is created from overlapping images so it may be biased or inaccurate if a feature is only captured from one side. Luckily, this is very easy to do – simply expand the area your flight plan. As in the last tip, it’s much easier to discard excess data than it is to capture more later!
4. Use GCPs for extra accuracy
Precise ground control points (GCPs) are strongly recommended. GCPs not only improve a project’s absolute accuracy but also ensure its relative accuracy as well. You can find more about relative and absolute accuracy in aerial mapping and what exactly is a GCP here.
Not sure where to start? Best practices dictate that a project’s control should be more accurate than the data it is controlling, therefore the accuracy of a GCP’s measurement should, at the very least, be better than the ground sampling distance of your image. We trust that you have taken the opportunity to estimate your project’s ground sampling distance by this stage.
However, image geotags measured with RTK/PPK can reduce the density or need for ground control points.
Whatever you choose to control your project’s results, we recommend that you include a handful of checkpoints to independently validate the accuracy of your results. Learn more about ground control points here.

5. Choose the right software for your needs
Choosing the software that is right for you depends on a number of factors. Pix4D offers dedicated tools for measuring distances, areas, and volumes, but you may have access to a different tool. Whatever software you choose to analyze your results, Pix4D can provide you with an accurate representation of your project area. Do you need more information? Find out how to improve your project's accuracy in Pix4Dmapper.
Bonus tip – ask for help
Not sure of something? Explore the Pix4D’s Knowledge Base or reach out to others on Pix4D’s Community. There may well be someone who has overcome the same issue you’re having.