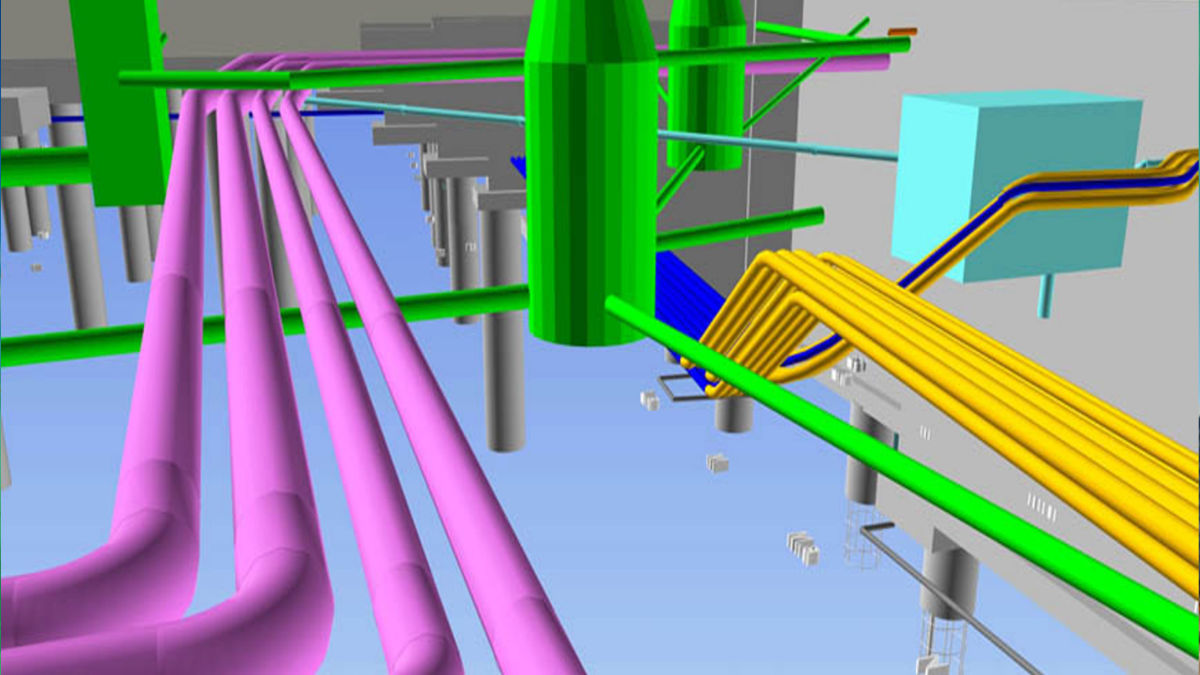
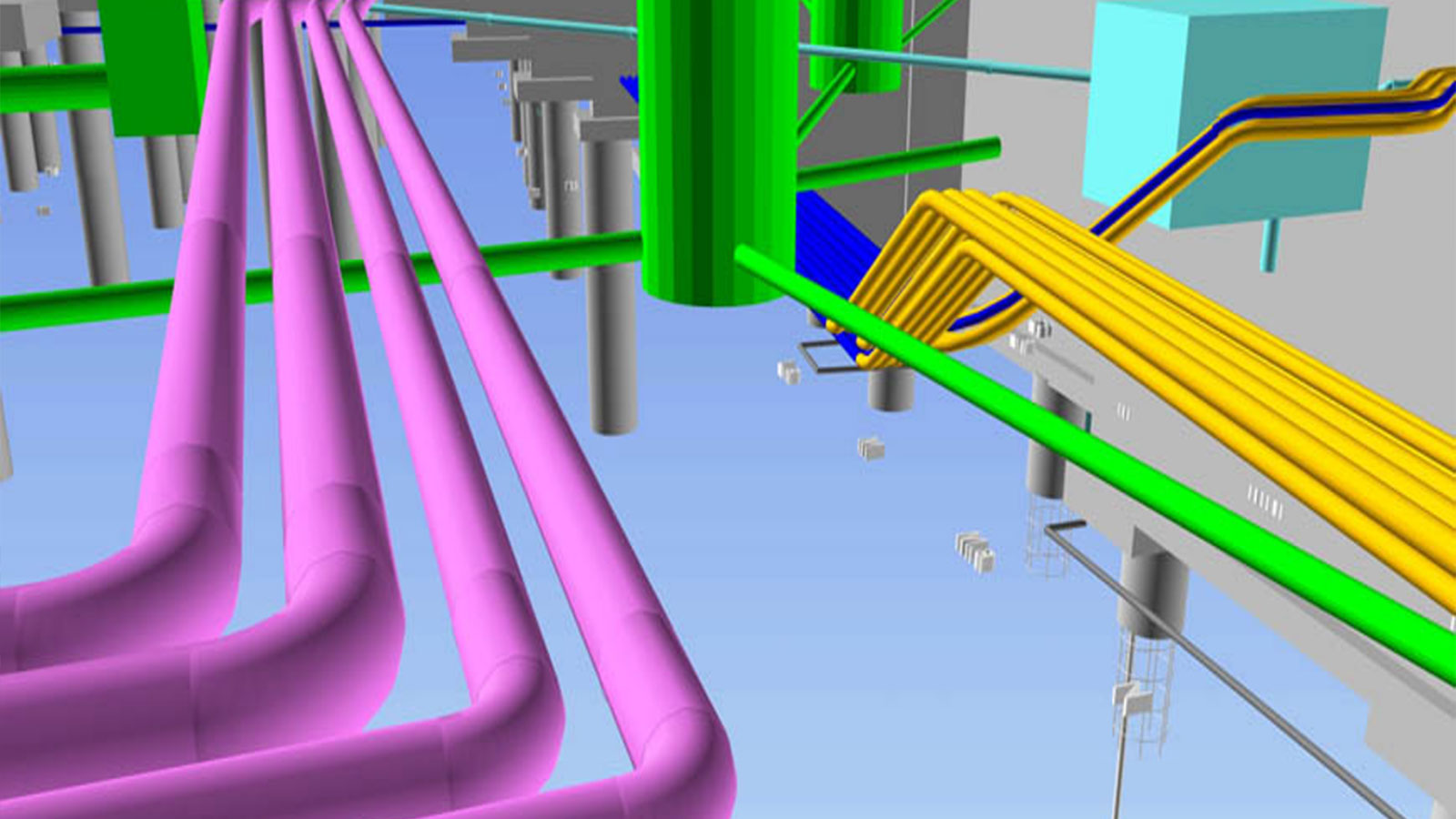
Mobile 3D scanning and the advance of digital construction
Governments worldwide are increasingly incorporating digital processes—such as BIM—into their building regulations. But why do policymakers deem digitizing construction so valuable, and what exactly is BIM?
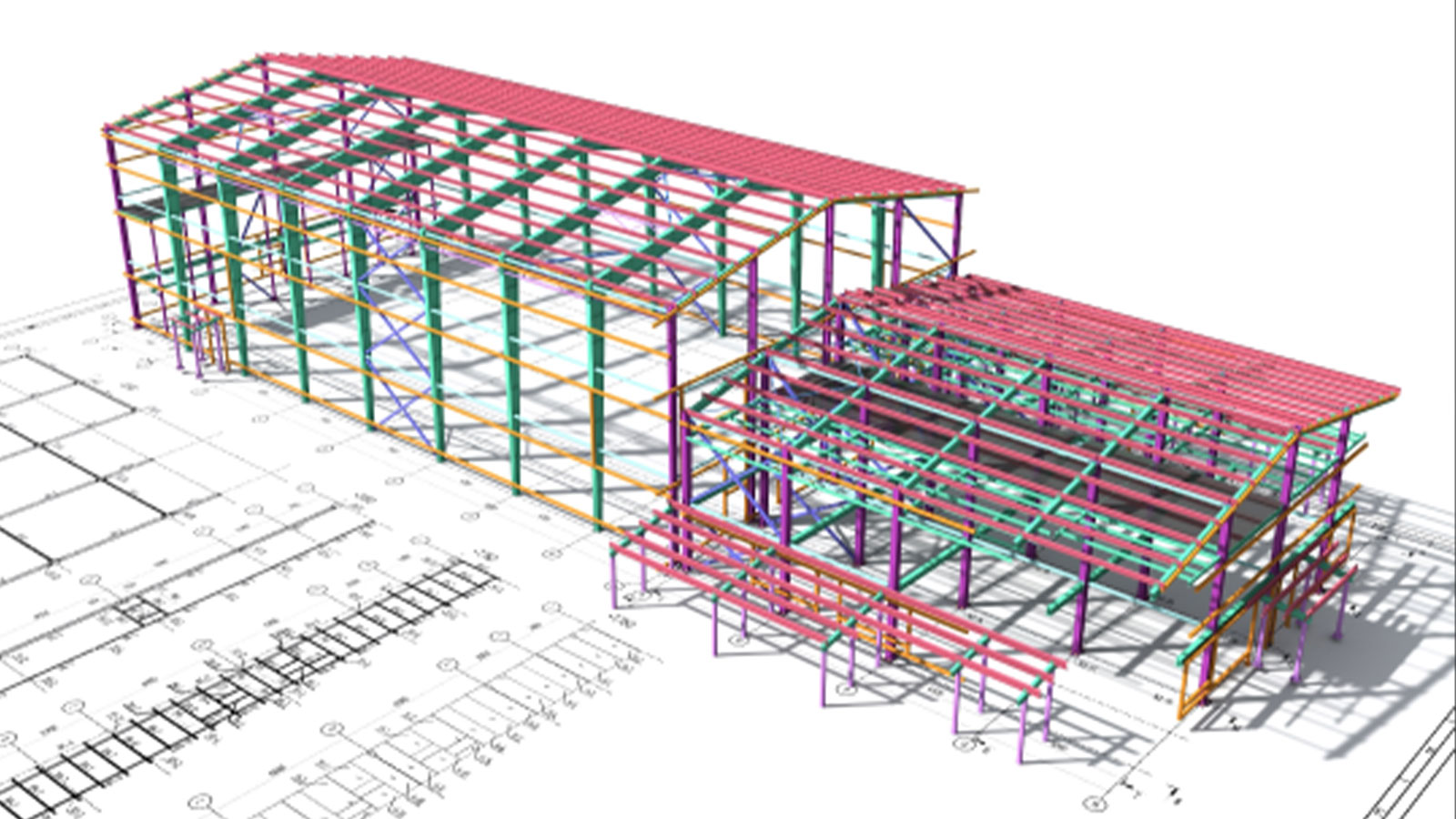
What is BIM?
BIM, or Building Information Modeling, is a digital process used in the building and construction industry. It's a collaborative approach that enables architects, engineers, surveyors, and construction professionals to work together within a single 3D model. BIM models include layers of information, ranging from architectural plans to utility layouts. Digital processes such as BIM are being increasingly adopted worldwide, with each country having a different implementation to enhance efficiency in their respective building industries.
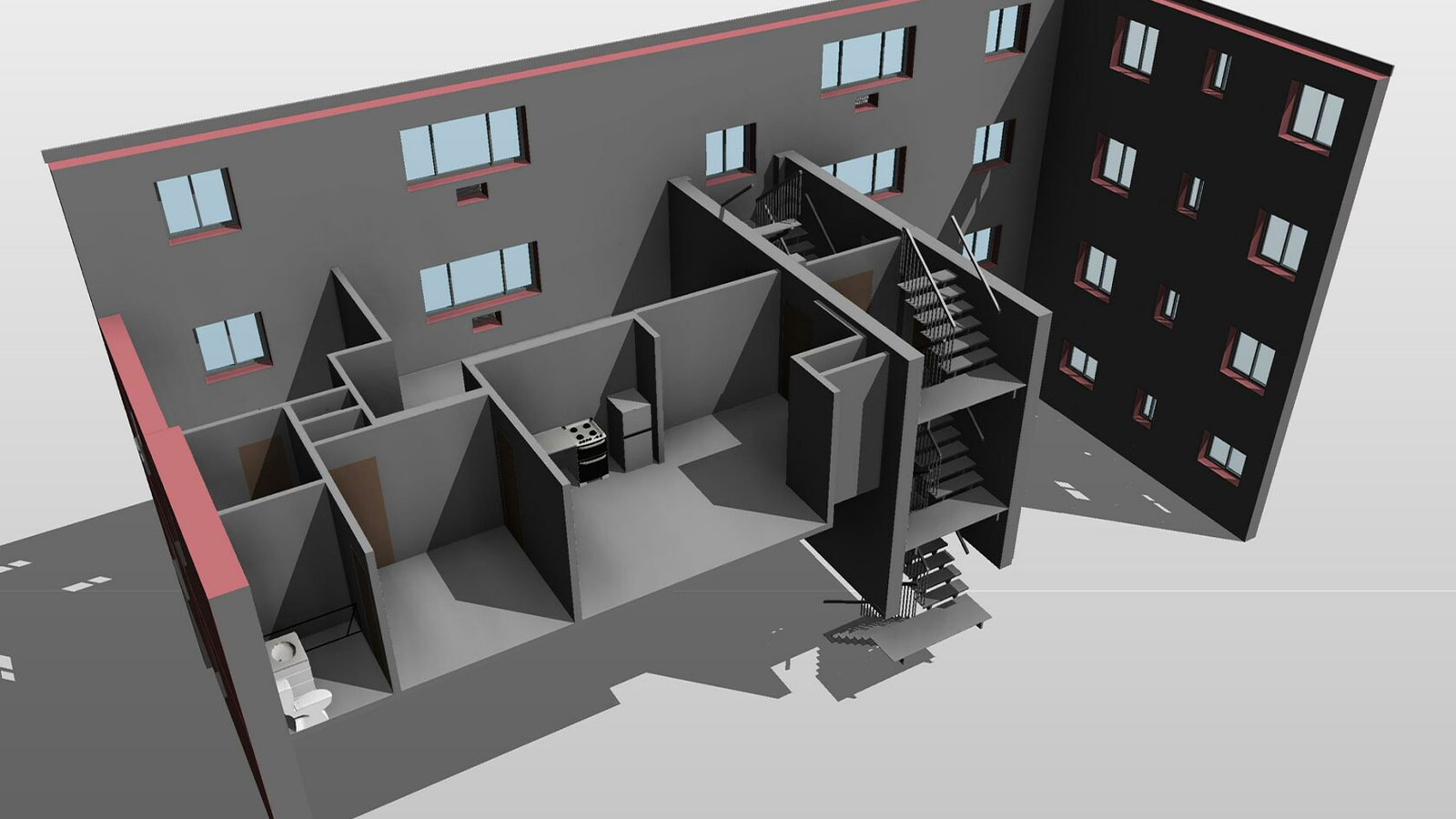

BIM levels explained
There are 4 BIM levels used to represent the level of digitization and collaboration on a project:
- Level 0 effectively no collaboration between teams, drawings are 2D CAD and the project is not digitized
- Level 1 a mixture of 2D and 3D with limited collaboration between stakeholders
- Level 2 collaborative working between stakeholders, using 3D CAD models
- Level 3 projects are fully collaborative. A single, shared 3D project is stored on a cloud server and used by all involved, resulting in a fully digitized lifecycle of the asset
Adoption of BIM globally
The UK, an early adopter since the 1980s, has made BIM level 2 mandatory for government projects. This approach has significantly improved project efficiency and savings (with an estimated national savings of 400 million pounds a year!)
While the USA was one of the early leaders in the development and implementation of BIM, the full uptake in the industry has been more challenging—a unified standard is missing.
In Germany, BIM is compulsory for government buildings and infrastructure, while France set a mandate for all critical underground infrastructure of urban areas to be mapped in 3D by 2019. Additionally, France has initiated a plan to implement the use of BIM in construction by 2022.
Beyond Europe, countries like Australia, Russia, Singapore, and China are also incorporating BIM into their construction practices, signaling a global shift towards digital construction.
Why digitization is important for construction
- Collaboration digitization fosters collaboration by providing all stakeholders with a centralized platform for storing and accessing project data, which makes the project work more efficient
- Digital documentation facilitates easy access, storage, and retrieval of crucial project information
- Reduces time and costs by using digital tools to spot possible errors in advance
- Sustainability allows stakeholders to assess environmental impacts and use resources more efficiently
- Documenting a project’s lifecycle using a digital process like BIM provides a record of the entire procedure, from preconstruction through to facilities management. This supports smooth handovers, continued management, and possible future renovations.
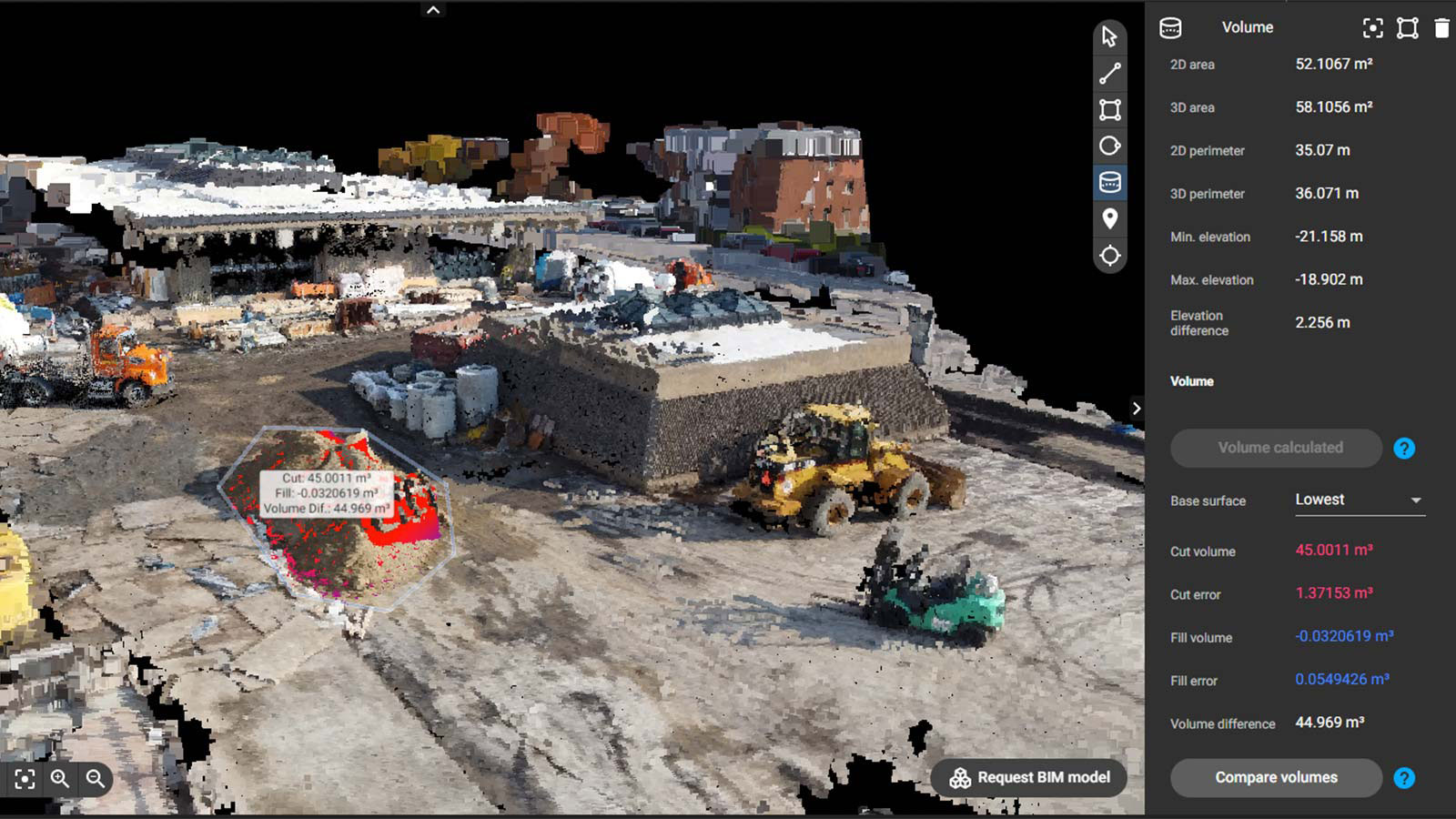
Mobile 3D scanning and construction
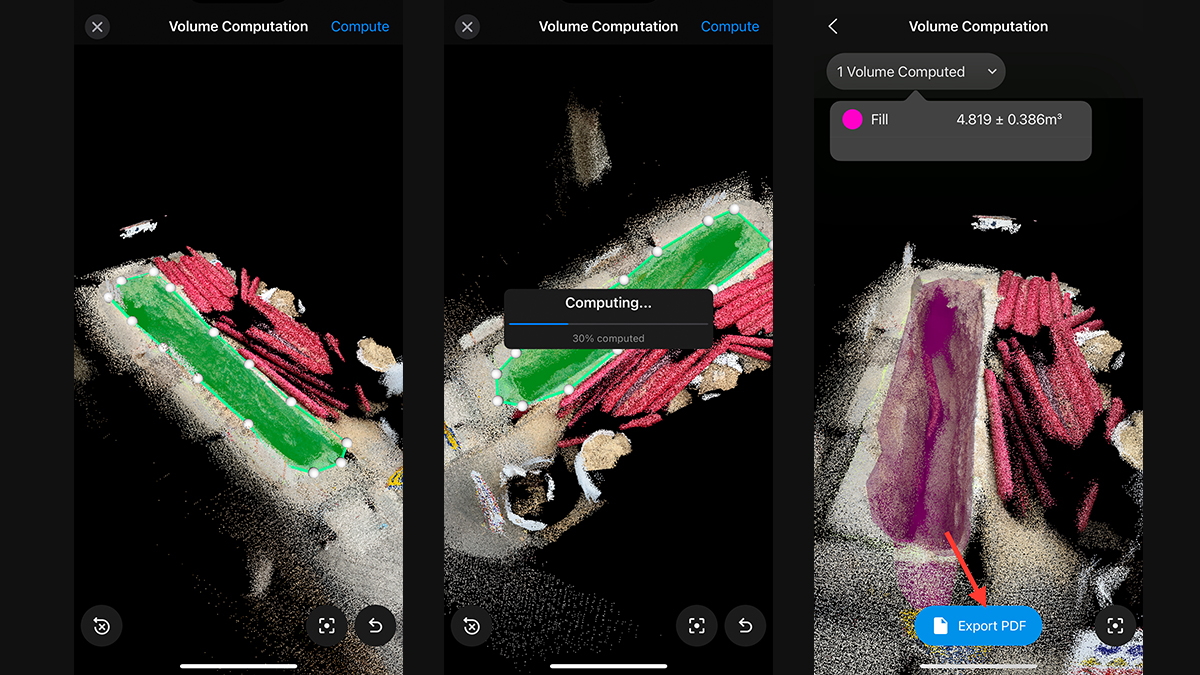
The adoption of smartphones is widespread. According to the 2023 Mobile Economy report 76% of the global population had smartphone connections in 2022, a figure that is expected to rise to 92% by 2030. The fact that most of the world’s population possesses a smartphone underscores the value of mobile scanning technologies like PIX4Dcatch, especially in the face of global integration of BIM-like processes into construction.
Traditional adoption of BIM methodologies often encounters barriers related to expertise and accessibility. However, mobile scanning offers an easy solution. PIX4Dcatch utilizes a powerful combination of LiDAR, photogrammetry, and RTK positioning, enabling users to achieve precise and accurate results. Scans can be automatically uploaded to PIX4Dcloud or exported to desktop software PIX4Dmatic, where stakeholders can work collaboratively on a 3D model.
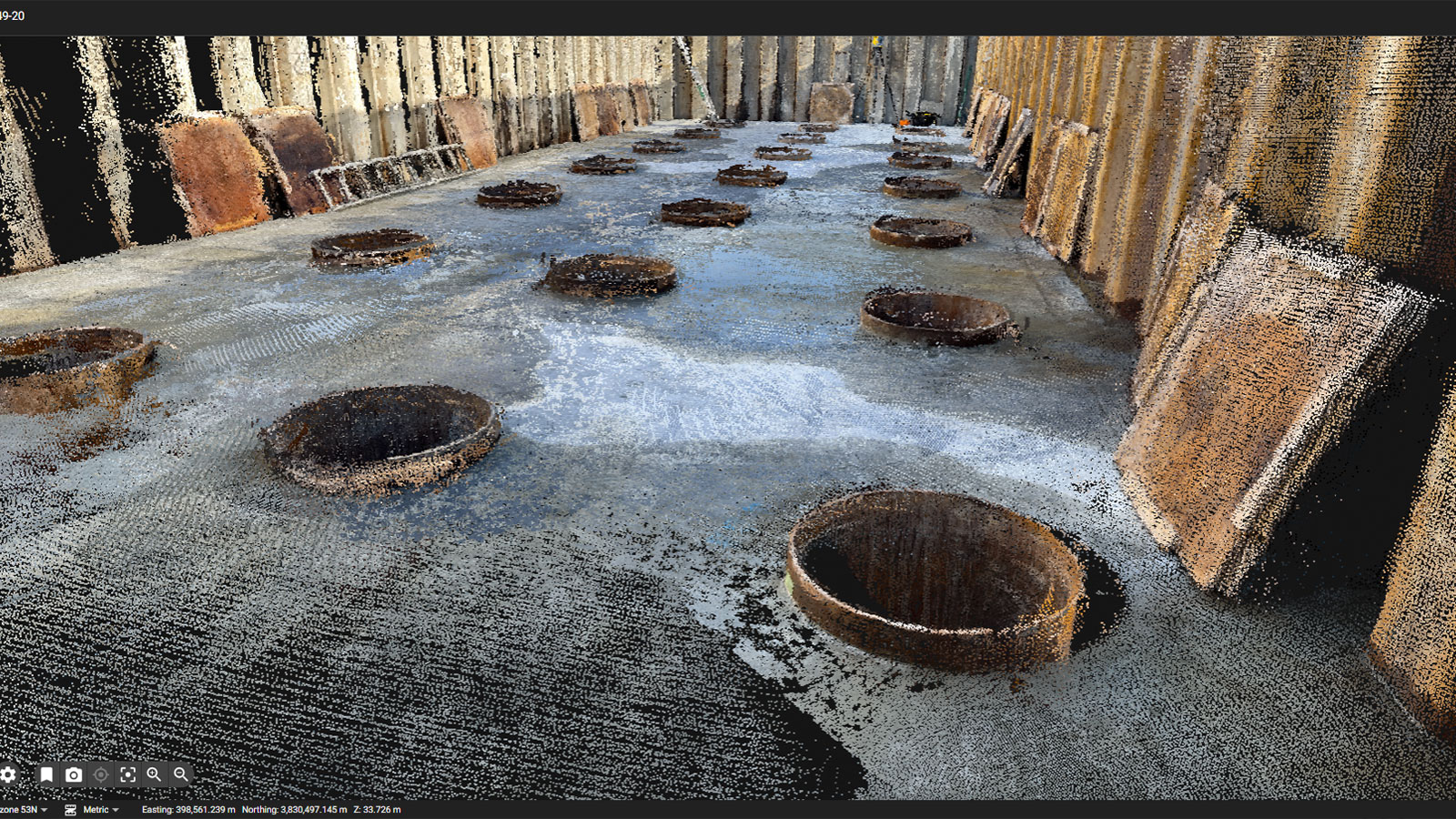

The tool is intuitive and requires minimal training, making it accessible to a wide range of professionals in the construction industry. Moreover, PIX4Dcatch goes beyond basic scanning and offers advanced features such as augmented reality (AR) where users can interact with scanned sites in real-time, overlaying CAD designs onto the physical environment and documenting trenches, visualizing the utilities even after closure.
Surveys have seen construction professionals name smartphones and tablets as the technology providing them the most value on-site. PIX4Dcatch as a mobile scanning app, meets these needs and aligns with the global adoption of digital processes like BIM, offering a straightforward solution to the construction industry. Its user-friendly interface, high accuracy, and ease of use (the phone is already in your pocket!) make it an accessible and effective tool for digitizing the construction process.