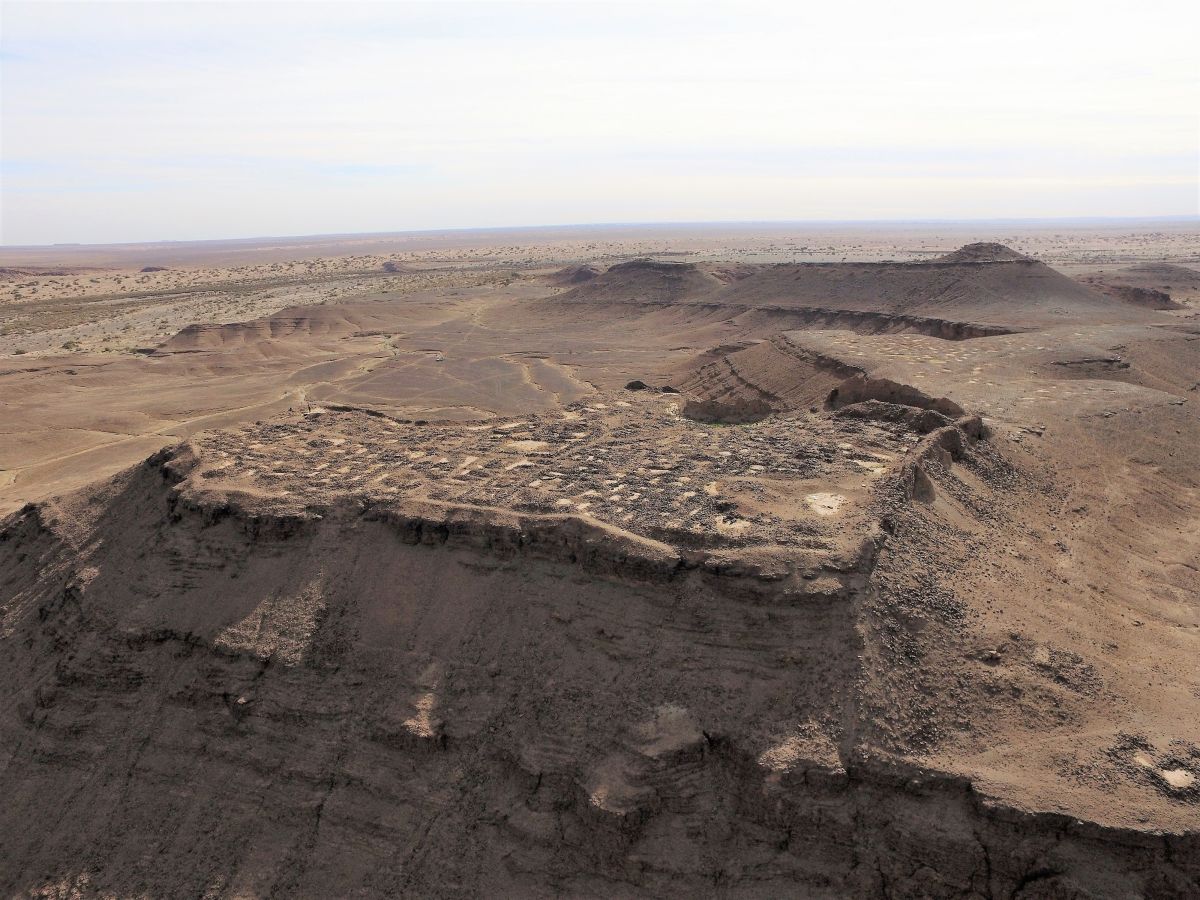
New tool for digital archaeology: drone mapping
The destruction of ancient structures by IS in Syria, as well as the collapse and damage of monuments in Nepal after a 7.8 earthquake garnered particular media attention in 2015, seeming to lend a more urgent feel to the protection and study of historical artifacts.
Archaeology not only faces the challenges of war and natural disaster, but often struggles to find funding in an uncertain economy, where the study is not always prioritized.
Drones are becoming ever more important tools not only for archaeology, but also for cultural heritage abbreviation. They are used to capture aerial images of archaeological sites and create accurate maps and 3D models which greatly help archaeologists document our history.
Digital archaeology and Digiart
The European project DigiArt, a consortium of seven organizations, is researching technology to address such challenges to: find efficient, low cost workflows to survey and digitally preserve sites; bring history closer to the public in innovative ways.As consumer drones become increasingly affordable, easier to use, and better quality, professionals in many domains are using them for mapping and 3D modeling.
In May, 2016, Pix4D and DigiArt partners Vulcan UAV, John Moores University, and GeoSense evaluated the drone mapping process by modeling King Philip II’s palace in Vergina, Makedonia, Greece, using four different consumer drones and Pix4D drone mapping technology.
Why use a drone as a tool for digitizing archaeology?
Accuracy
One of the important aspects of excavating an archaeological site is the ability to conduct both a precise survey and documentation of artifacts.
High-accuracy GNSS devices are already used to survey sites, therefore, it’s interesting to evaluate the accuracy of models produced with consumer drones to see if they can compete.
Education
There is increasing interest in using 3D models of archaeological sites for educational purposes. Archaeologists and cultural organizations want to show excavation results to the public, as well as make the sites easily understandable.
By overlaying 3D models of the current environment with the projected ancient situation (virtual reality), visitors can gain a better understanding of people from the past.
Comparing consumer drones
The more lightweight a drone is, the easier it is to transport and less threatening it seems to objects and people. However, this lightweight can also mean a slower flight and less stability in wind.
| Drone | Price range | Weight |
| Parrot Bebop 2 | ~$500 | 500g |
| DJI Phantom 3 | ~$1,000 | 1.280kg |
| DJI Inspire 1 x3 | ~$3,000 | 2.935kg |
| DJI Inspire 1 x5 | ~$5,000 | 3.500kg |
Prices are indicative only. Check manufacturer's websites for details.
Where the camera is concerned, the Bebop 2 has a 180° fisheye lens, with the other drones equipped with perspective cameras. Pros and Cons are weighed based on the budget available, conditions being dealt with, and accuracy needed.
Flying the past
In order to manage the flight and direct a proper flight plan, the team used Pix4Dcapture, a drone flight app that automatically captures images of an area at high overlap for model creation in photogrammetry software.
How it works:
- Open Pix4Dcapture and select your drone
- Select the area to map
- Start mission (drone automatically flies over selected area collecting optimal mapping photos)
- After the last photo is taken, drone automatically flies to home point and lands
- Transfer the images to Pix4Dmapper photogrammetry software for processing
Model comparison of an archaeology site – textured triangle mesh
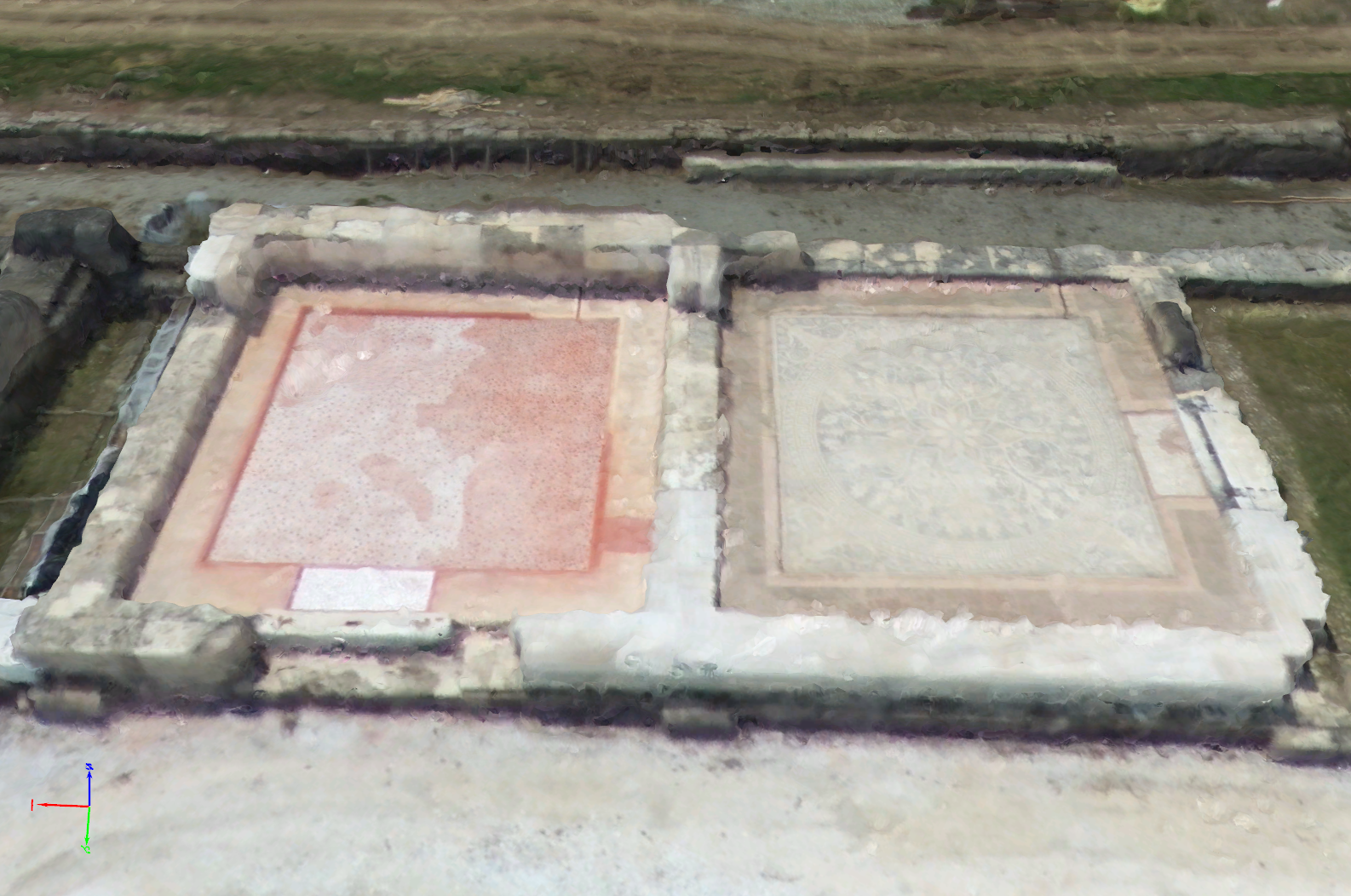
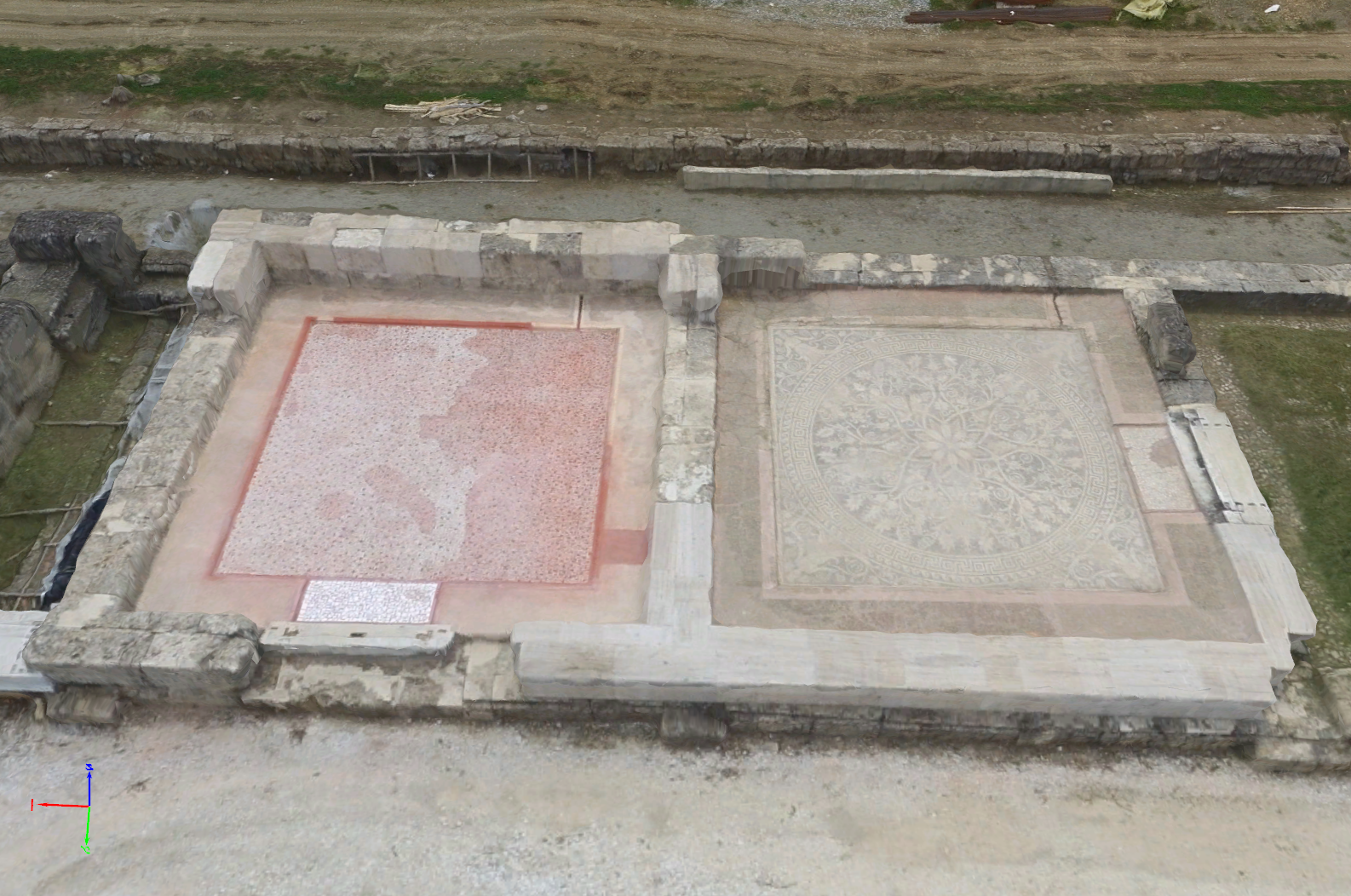
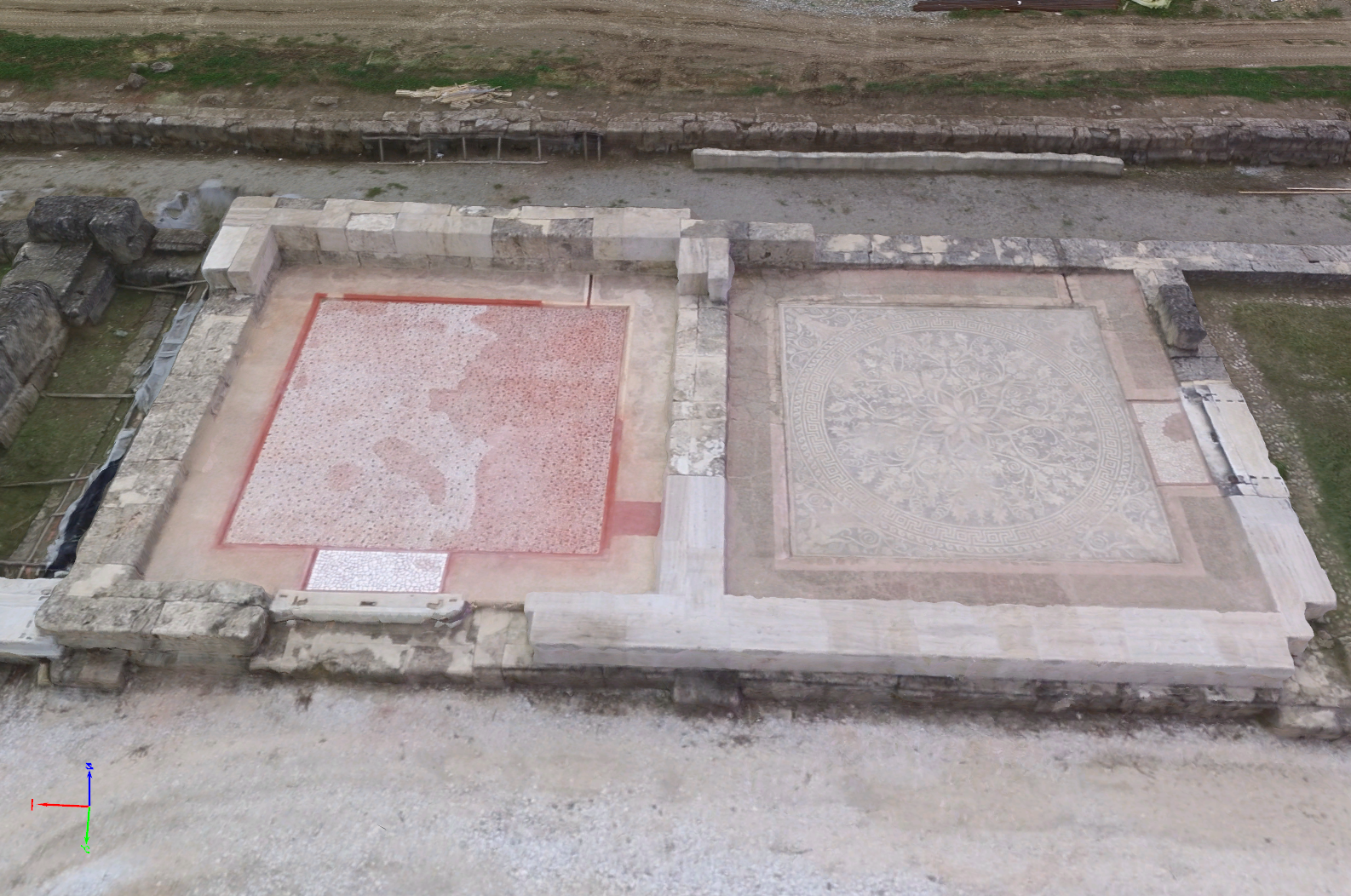
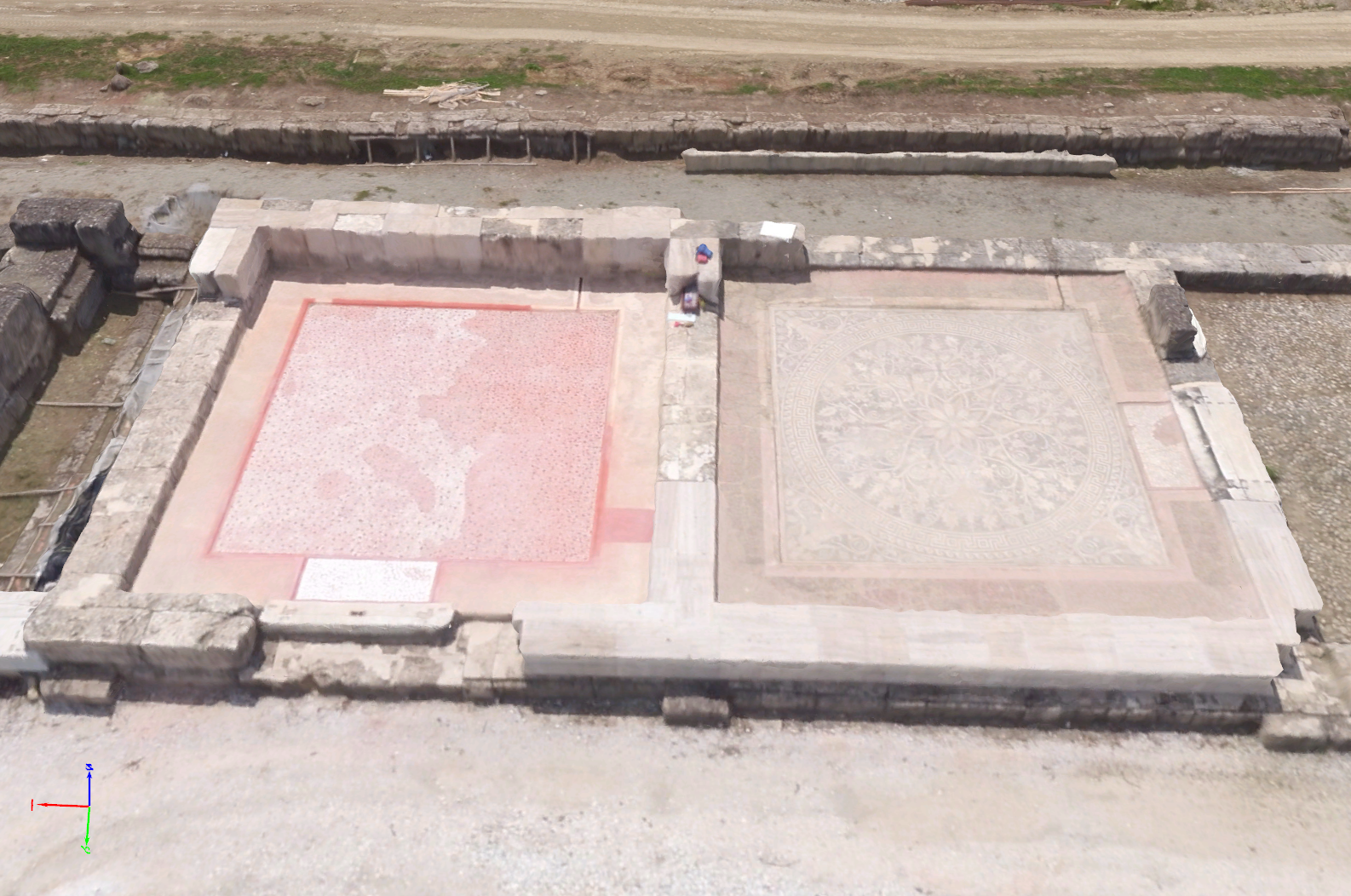




Accuracy of Results
25 ground truth points were measured, with 5 used as ground control points to ensure the accurate location and 20 used as check points. Absolute accuracy of these check points is evaluated against those measured by a high accuracy GNSS device.
| Images | Flights | Flight Time (min) | GSD (ha) | RMS error (m) 20 points (x, y, z) | |
| Bebop 2 (4 flights) | 360 | 4 | 67 | 9.61 | 0.003, 0.002, 0.004 |
| Phantom 3 | 112 | 1 | 10 | 1.29 | 0.074, 0.054, 0.077 |
| Phantom 3 (rolling shutter fix) | 112 | 1 | 10 | 1.29 | 0.005, 0.003, 0.006 |
| Inspire 1 x3 | 113 | 1 | 9 | 1.32 | 0.005, 0.007, 0.009 |
| Inspire 1 x3 (rolling shutter fix) | 113 | 1 | 9 | 1.32 | 0.003, 0.002, 0.003 |
| Inspire 1 x5 | 111 | 1 | 6 | 1.54 | 0.667, 0.421, 0.823 |
| Inspire 1 x5 (rolling shutter fix) | 111 | 1 | 6 | 1.52 | 0.024, 0.028, 0.058 |
One Bebop 2 dataset, consisting of 4 flights, used the Pix4Dcapture feature, which enables drones requiring battery changes to map larger areas. The check point error was from 2-5 cm on average. Globally, the accuracy is expected to be around 15-20 cm (1.5-2x the GSD) for the Bebop 2 dataset, but the accuracy for this drone can be harder to assess. The 180° fisheye lens results in a very non-uniform GSD, i.e. the accuracy in the center is much better that in the peripheral of the images, and the final result depends largely on how the scene is covered.
The results of the DJI datasets are quite similar. All DJI cameras have a rolling shutter, which can be compensated for in Pix4Dmapper by applying a rolling shutter correction which improves accuracy in general cases. Altitude for the flights was taken around 40 m, chosen to achieve a GSD of about 1-2 cm. Of course, it is good to keep in mind that flight results are not comprehensive and depend on several factors, including variations in drone speed and height, and weather conditions.Drone applications in archaeology
After evaluating the different qualitative and quantitative results from four different consumer drones and Pix4Dmapper, we concluded that archaeological sites can be mapped at relatively low cost and an acceptable accuracy. Depending on a project, organization, or professional’s needs, this workflow enables mapping with consumer drones to fulfill both documentation/excavation process and the educational purposes. One of the greatest advantages of drone mapping is that we can document even the most complex archaeological sites.
The DigiArt Project
What if instead of simply looking at artifacts in museums, we could be virtually transported to the time the artifact was created, and actually see it in its original context? This is the idea that DigiArt, a European project, is trying to realize, by changing the way people view and experience artifacts. By communicating the research done by archaeologists and making said research accessible to the public in a visual and interactive way, they get people excited about history and show the importance of funding archaeology.



